We define to be a permutation of the first natural numbers in the range . Let denote the value at position in permutation using -based indexing.
is considered to be an absolute permutation if holds true for every .
Given and , print the lexicographically smallest absolute permutation . If no absolute permutation exists, print -1.
Example
Create an array of elements from to , . Using based indexing, create a permutation where every . It can be rearranged to so that all of the absolute differences equal :
pos[i] i |pos[i] - i| 3 1 2 4 2 2 1 3 2 2 4 2
Function Description
Complete the absolutePermutation function in the editor below.
absolutePermutation has the following parameter(s):
- int n: the upper bound of natural numbers to consider, inclusive
- int k: the absolute difference between each element's value and its index
Returns
- int[n]: the lexicographically smallest permutation, or if there is none
Input Format
The first line contains an integer , the number of queries.
Each of the next lines contains space-separated integers, and .
Constraints
Sample Input
STDIN Function ----- -------- 3 t = 3 (number of queries) 2 1 n = 2, k = 1 3 0 n = 3, k = 0 3 2 n = 3, k = 2
Sample Output
2 1
1 2 3
-1
Explanation
Test Case 0:
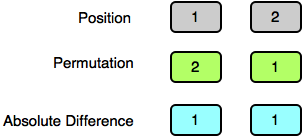
Test Case 1:
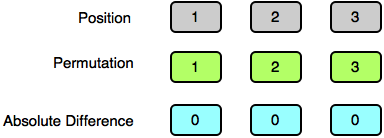
Test Case 2:
No absolute permutation exists, so we print -1 on a new line.
SOLUTION:




No comments:
Post a Comment